The bull call spread strategy is used by investors who believe the price of the stock will go up in the near future. It’s a great strategy to use if you want limited downside risk and defined profits targets.
Summary
- The bull call spread strategy has limited-risk as well as limited-profit
- The strategy benefits from an increase in the price of the stock
- A bull call spread has a higher potential profit than a higher potential loss
- Ideal for high volatility environments
What is the Bull Call Spread Strategy?
A bull call spread is a limited-risk, limited-profit strategy used by investors who believe price of the stock will rise modestly in the short term. It uses two separate call options contracts for the same expiration date to create a price range or “spread” to profit from.
This strategy tends to be used during periods of high volatility. The gains and losses are capped due to the upper and lower strike prices.
Bull Call Spread Construction
A bull call spread consists of buying an at-the-money call option and simultaneously selling a higher out-of-the-money call option for the same expiration date. As a result of creating the spread, you will pay a net debit to enter the trade. Since you end up paying a debit to enter into this trade, it is oftentimes referred to as a “bull call debit spread”.
- Buy ATM call option
- Sell OTM call option
By selling an OTM call option you reduce the cost of creating a bullish options position, but at the same time eliminate the opportunity to make a larger profit in the chance that the price of the stock goes up sharply.
Bull Call Spread Payoff Diagram
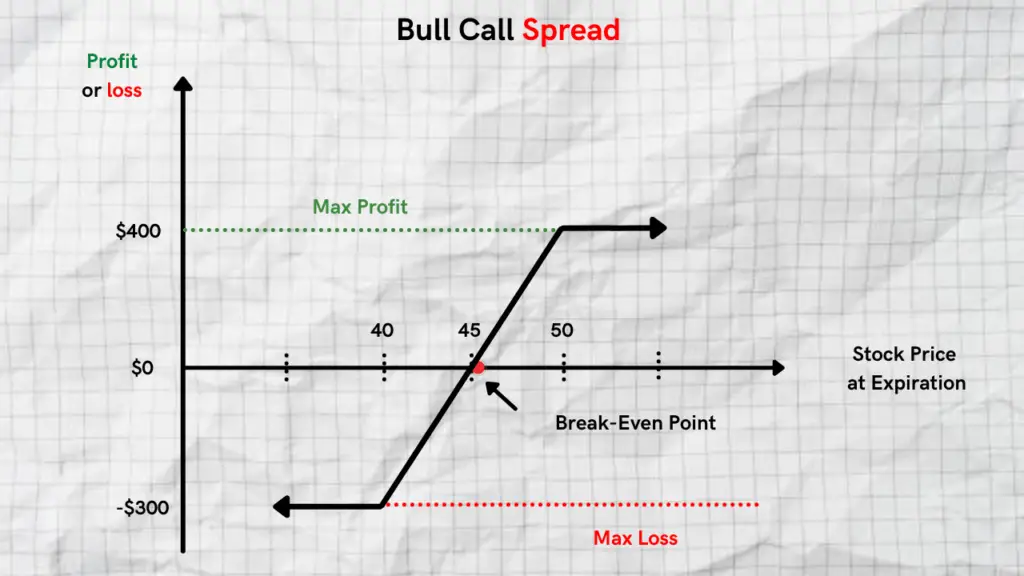
Bull Call Spread Risk Profile
Before you decide to trade this strategy, it’s important to be well aware of its maximum profit, maximum loss, along with its break-even points.

Limited Profit Potential
Although this strategy has limited profit potential, it’s higher than its maximum loss potential. The bull call spread strategy reaches its maximum profit potential once the price of the stock moves ABOVE the higher strike price (the sold OTM call option).
Max Profit = The strike price of the short call – Strike price of the long call – net debit paid
The wider the widths of your spread, the larger your potential profit, and at the same time the lower your probability of profit.
Limited Loss Potential
A great component to bull call debit spreads is the fact that they have a fixed level of risk. The max loss is limited to the debit paid for the trade. The strategy will result in a loss if the price of the stock goes down by the expiration date.
Max Loss = Net Premium paid + Broker Commissions
It’s a great strategy to use if you want a fixed level of risk to the downside, but have a higher payout to the upside if the stock price rallies.
Break-Even Point
It’s important to know the break-even price for bull call spreads if you want to get out of the trade earlier than you anticipated.
Break-even = strike price of the long call + net premium paid
Knowing the different risk parameters associated with this strategy is key to managing your trade effectively if the market turns against you.
Bull Call Credit Spread Example
Let’s assume that the price of Microsoft (MSFT) is currently trading at $225 per share. You have reason to believe that price will rise sharply to the upside within the month. As such, you decide to enter into a bull call debit spread. Below is the trade.
- Buy $225 call option (-$4.50)
- Sell $228 call options (+$3.50)
As a result of getting into this trade, you end up paying $1.25.
Max Profit = $1.75
The max profit on a bull call spread is the strike price of the short call – strike price of the long call – net debit paid.
In this scenario, your max profit would be $1.75 or $175 (100x $1.75)
Strike Price of the Short Call = $228
Strike Price of the Long Call = $225
Net Debit Paid = $1.25
Max Profit = $1.75
Max Loss = $1.25
With bull call spreads, the max loss is limited to the net debit paid to enter the trade. In this example your max loss would be $1.25
Break-even = $226.25
As previously stated the breakeven price for a bull call debit spread is the strike price of the long call + net premium paid
Strike price of long call = $225
Net debit paid = $1.25
Break-even price = $226.25
Knowing this components to an options spread is very important in case the price of the stock moves sharply in your favor. If it does you can exit the trade before your expiration date.
Pros and Cons of Trading Bull Call Spreads
| Pros | Cons |
| Fixed level of risk ( max loss is limited to the debit paid) | Limited profit potential ( gains are capped if the price of the stock rallies above the higher call strike) |
| It’s a cheaper way to go long a stock than buying a call option | The probability of profit reduces the wider the width of the strikes |
| Max profit potential is higher than the max possible loss | You have to pay out a debit instead of collecting a credit |
Bull Call Assignment Risk
It’s important to note that to mitigate the potential assignment risk associated with bull call spreads, it’s important to close your trade before the expiration date IF it has a high probability to expire between your two strikes.
If the price of the stock is between your two strikes at expiration, you will be assigned 100 shares of stock short at the short call strike price.
Going from our example trade above, if the price of the stock is at $227 at expiration, you would be assigned 100 shares short of MSFT from your broker. This means that your bullish bet has now turned into a bearish bet after the assignment has taken place. This is why it’s important to pay close attention to the price of the stock as it approaches the expiration date.
FAQ’s
Is a bull call spread better than a bull put spread?
Not necessarily. Although the two strategies both have a bullish approach, the bull put spread receives a credit while the bull call spread pays out a debit.
Related Reading