Stagflation is an economic phenomenon that has a serious global impact on consumers and businesses. If nations fail to appropriately adjust and manage their monetary policy, the impact of stagflation can push economies into a recession and cause political and societal instability. Let’s take a look at what you need to know about stagflation and how it can impact the economy on a global scale.
Summary
- Stagflation is a term used to describe an economy with rising levels of inflation, high unemployment, and slowing economic growth
- Stagflation is mainly caused by poor economic policy and unexpected supply chain shortages and shocks
- If stagflation is not managed effectively by governments it can cause the economy to spiral into a recession
What is Stagflation?
In economics, stagflation is a term used to describe an economy with rising levels of inflation, high unemployment rates, and an overall slowing of economic growth. The term “stagflation” is a combination of the word stagnation – meaning a lack of activity, growth, or development and the term inflation – meaning an increase in prices of goods and services. Stagflation is meant to describe an economy that is breaking down and heading towards a period of economic constriction that has an overall negative impact on consumers and businesses.
With stagflation, consumers and businesses are forced to tighten their spending to battle the effects of inflation. This spending adjustment further fuels inflation over the long term and causes a further economic meltdown that can eventually lead to a recession.
What Causes Stagflation?
There are many causes that can lead to stagflation, however, the main leading causes of stagflation are a combination of poor fiscal and monetary policy along with extended shocks to supply chains.
Poor Fiscal and Monetary Policy
In the U.S. the Federal Reserve suppressed interest rates to historical lows for an extended period of time which led to high real estate prices, construction costs, gas prices, and more. Covid-19 certainly didn’t help and the Federal Reserve issued stimulus in order to help people make ends meet.
Extended Supply Chain Shocks
A supply chain shock is when there is an unexpected and drastic reduction in the economy or specific sector to produce goods and services at reasonable prices. Throughout the pandemic and after the pandemic, there have been massive supply shocks in areas such as:
- Labor – Manufacturing, food services, hospitals workers, construction workers
- Goods – Semiconductor shortages, baby-food formula shortages, toilet paper shortage
Another contributing cause to stagflation is the rise in the price of oil. Battling the causes of stagflation is a very difficult task for monetary policymakers.
Stagflation Graph and Diagram
To make sense of stagflation, it’s important to be able to visualize its effects on prices, demand, and supply. Below is a supply and demand diagram illustrating higher oil prices.
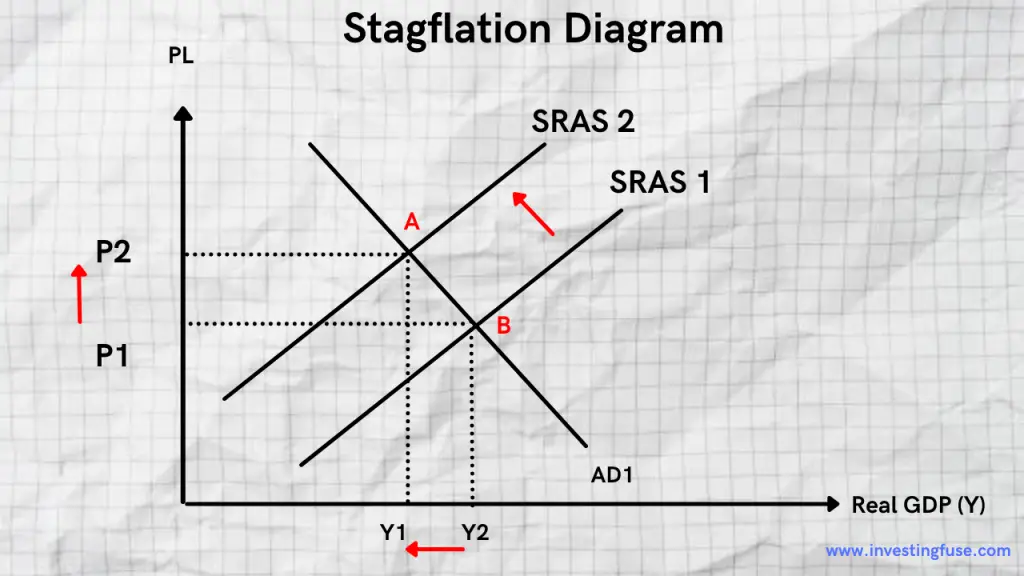
SRAS = Short-Run Aggregate Supply
P = Price
AD = Aggregate Demand
Y = Real GDP
As you can see, higher oil prices increase costs of production, shifting SRAS higher to the left. In addition, Real GDP drops to the left from Y1 to Y2 and the price goes up from P1 to P2.
Why is Stagflation Bad?
The trickle-down effects of stagflation can cause extended economic duress. Stagflation is bad because it slows down economic growth which can cause an increase in unemployment. However, it does not naturally result in rising prices. This is why it’s harmful to the overall economy.
A general increase in unemployment tends to result in lower consumer spending which tends to level off higher prices and with a high enough unemployment rate, prices will reduce.
How to Battle Stagflation?
There is no direct way to battle the effects of stagflation. The best thing governments can do is improve their monetary policy to avoid ever going into stagflation. To get an economy out of a period of stagflation, productivity has to increase to a level where there is growth without the negative effects of inflation. This is difficult to accomplish with just monetary policy and increasing interest rates.
Governments have to take a closer look at their monetary policy and structure it in a way that incentivizes growth without the impact of inflation.
Consequences of Prolonged Stagflation
The economic impact of prolonged stagflation can have devastating effects on economies. Below are some of the negative effects of prolonged stagflation if governments fail to take appropriate action.
- Higher unemployment rates
- Lower wages
- Decreased consumer purchasing power
- Reduced investment by businesses
- Galloping inflation levels
- Recession or depression
The longer that the effects of stagflation linger on an economy, the worse the impact will be on consumers and businesses.
Inflation vs. Stagflation
Generally speaking, inflation is seen as a negative economic effect by the general public because it makes the money you save today less valuable in the future. It reduces consumers’ purchasing power and can cause overall economic growth to slow down. It also affects employment, supply chains, investments, retirement, and more.
The main difference between these two is the impact on economic growth. Inflation tends to be paired with economic growth and is often a result of a growing or developing economy. Conversely, if an economy heads toward recession inflation slows down. However, with stagflation, inflation is high and economic growth reduces. It’s a rare economic phenomena.
History of Stagflation
1970
The 1970 stagflation comes following Richard Nixon’s imposition of wage and price controls on August 15th of 1971. An initial wave of cost-push shocks in commodities was the scapegoat for high prices. This was the “Nixon Shock”.
1973
In 1973 the second major shock was the 1973 oil crisis. This occurred when OPEC (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries) held a majority portion of the global supply of oil. They proclaimed an oil embargo that targeted nations that has supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War.
Conclusion
As you can see, the impact of stagflation can have a serious impact on businesses, consumers, and global economies. It can take a very long time for economies to recover and for consumers to get back to a level of normal. As a consumer, it’s important to have to know how its effects can change your spending and saving habits.
